This is indeed the greenhouse gas that is currently producing the greatest impact on the Earth's rapidly changing climate But it is far from the only one making its mark, and for mitigating climate change it's important to be able to compare the effects of the various gases that contribute to warming the planetYou are going to email the following "Greenhouse Effect" Definition Message Subject (Your Name) has forwarded a page to you from Science Message Body (Your Name) thought you would like to see this page from the ScienceThe effect of increased greenhouse gas concentrations;

Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society
What is the greenhouse effect easy definition
What is the greenhouse effect easy definition- The "natural greenhouse effect" (increase of earth temperatures by 33°C) is a myth IRactive gases do not act "like a blanket" but rather "like a sunshade" They keep a part of the solar energy away from the earth's surface " The roots of the greenhouse effect concept lie in the 19th century, when French mathematician Joseph Fourier calculated in 14 that the Earth would be much colder if it had no atmosphere In 16, Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius was the first to link a rise in carbon dioxide gas from burning fossil fuels with a warming effect



1
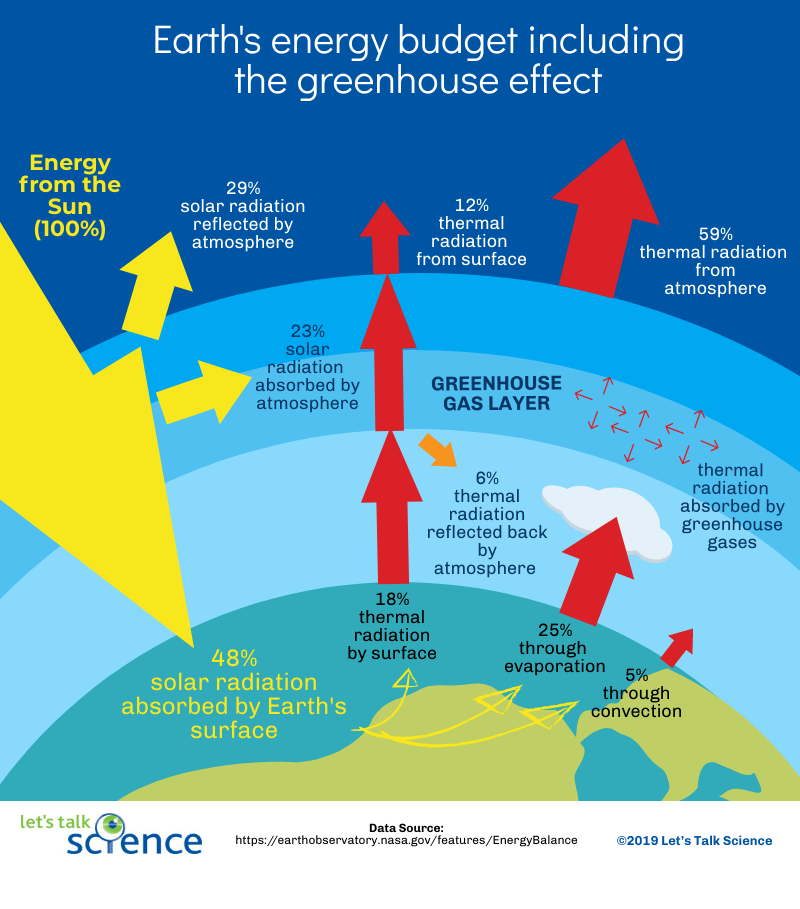
Adding more greenhouse gases to the atmosphere enhances the effect, making Earth's surface and lower atmosphere even warmer Image based on a figure from US EPA ( larger version) Greenhouse gases affect Earth's energy balance and climate The Sun serves as the primary energy source for Earth's climate The greenhouse effect arises from Earth's atmosphere Visible light from the sun , as well as invisible ultraviolet and infrared wavelengths, can penetrate theThen release energy in all directions, which keeps the Earth warm An example of greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane and water vapour Infrared radiation from the Sun is
Many Earth scientists and meteorologists, however, were becoming alarmed about the growing evidence supporting the notion of an enhanced greenhouse effect In 1979 the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) established its World Climate Program to collect data and research the complex components of the Earth's climate systemFigure 71 Rise in the concentrations of greenhouse gases since the 18th century As we will see in section 73, simple theory shows that a rise in greenhouse gases should result in surface warming;The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gases—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinated gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Greenhouse gases let the sun's light shine onto the Earth's surface, but they trap the heat that reflects back up into the atmosphere
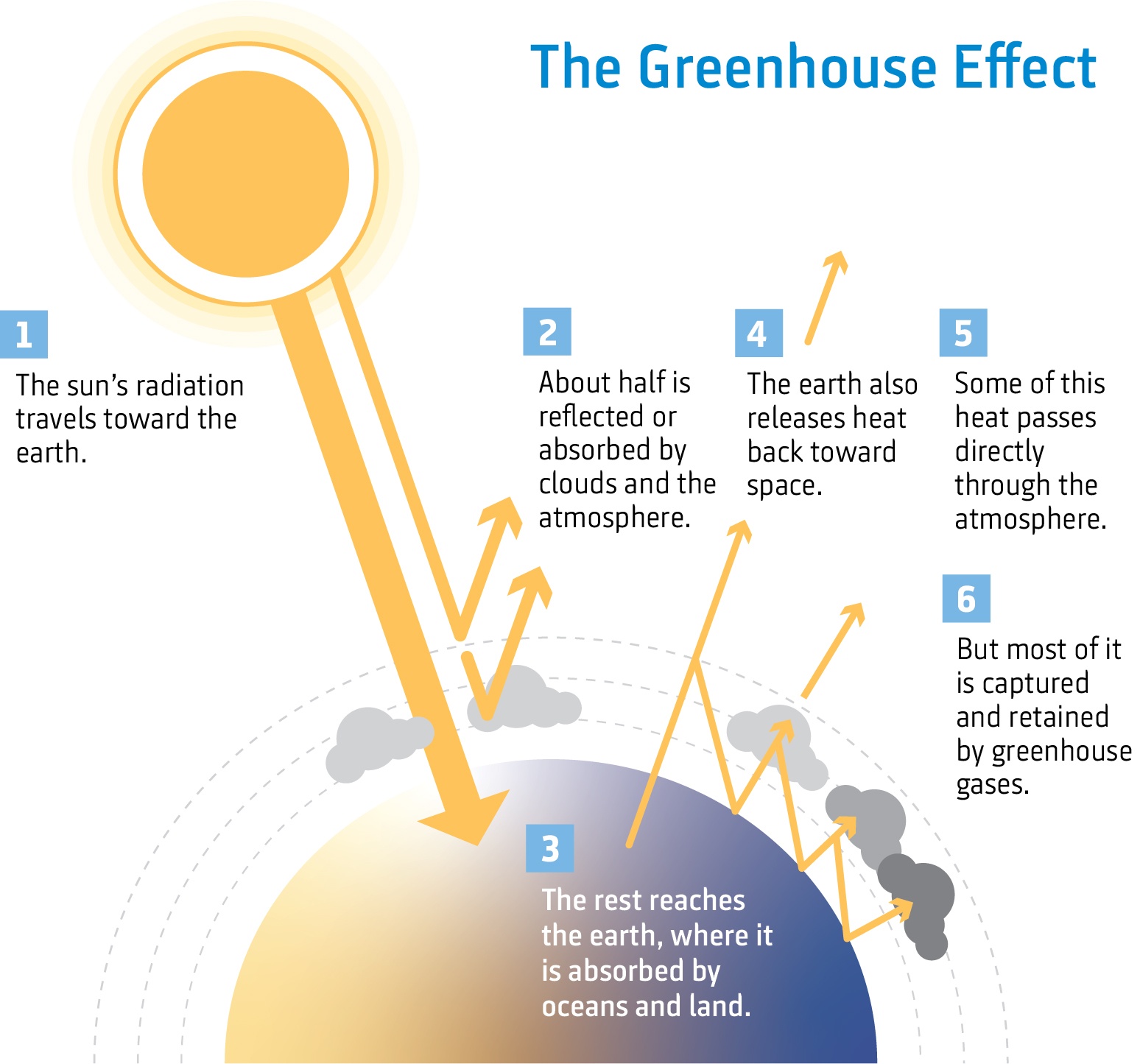
The greenhouse effect The exchange of incoming and outgoing radiation that warms the Earth is often referred to as the greenhouse effect because a greenhouse works in much the same way Incoming UVThe greenhouse effect causes some of this energy to be waylaid in the atmosphere, absorbed and released by greenhouse gases Without the greenhouse effect, Earth's temperature would be below freezing It is, in part, a natural process However, Earth's greenhouse effect is getting stronger as we add greenhouse gases to the atmosphere Weather is a specific event—like a rainstorm or hot day—that happens over a few hours, days or weeks Climate is the average weather conditions in a place over 30 years or more NASA has observed that Earth's climate is getting warmer




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Live Science
"The greenhouse effect makes our planet habitable," says Graeme Stephens, director of the Center for Climate Sciences at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) "The climate is just right on Earth because of its atmosphere" "In theseDefine greenhouse effect greenhouse effect synonyms, greenhouse effect pronunciation, greenhouse effect translation, English dictionary definition of greenhouse effect greenhouse effect Energy radiated by the sun converts to heat when it reaches the earth that mimics Earth's atmospheric greenhouse effect Through modeling and experimentsGreenhouse gases such as methane, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and water vapor significantly affect the amount of energy in the Earth system, even though they make up a tiny percentage of Earth's atmosphere Solar radiation that passes through the atmosphere and reaches Earth's surface is either reflected or absorbedReflected sunlight doesn't add any heat to the Earth




Sustainable Energy The Future Is Clear We Must Move Forward With Sustainable Energy Green Planet Ethics



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface An amplified greenhouse effect is driving the changes, according to Myneni Increased concentrations of heattrapping gasses, such as water vapor, carbon dioxide and methane, cause Earth's surface, ocean and lower atmosphere to warm Warming reduces the extent of polar sea ice and snow cover, and, in turn, the darker ocean and land surfacesThe greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Effect Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation
Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect is a process by which thermal radiation from a planetary surface is absorbed by atmospheric greenhouse gases, and is reradiated in all directions Since part of this reradiation is back towards the surface and the lower atmosphere, it results in an elevation of the average surface temperature aboveGreenhouse Earth Overview of greenhouse Earth A "greenhouse Earth" is a period in which there are no continental glaciers whatsoever on the planet Additionally, the levels of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases (such as water vapor and methane) are high, and sea surface temperatures (SSTs) range from 28 °C (4 °F) in the tropics to 0 °C (32 °F) in the polar regionsGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases,



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The retention of part of the Sun's energy in the Earth's atmosphere in the form of heat as a result of the presence of greenhouse gases Solar energy, mostly in the form of shortwavelength visible radiation, penetrates the atmosphere and is absorbed by the Earth's surface The greenhouse effect is a good thing It warms the planet to its comfortable average of 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius) and keeps life on earth, well, livable Without it Earth as a closedup greenhouse would soon grow to be ghastly!



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Global Warming S 1 Science Planet Earth Topic
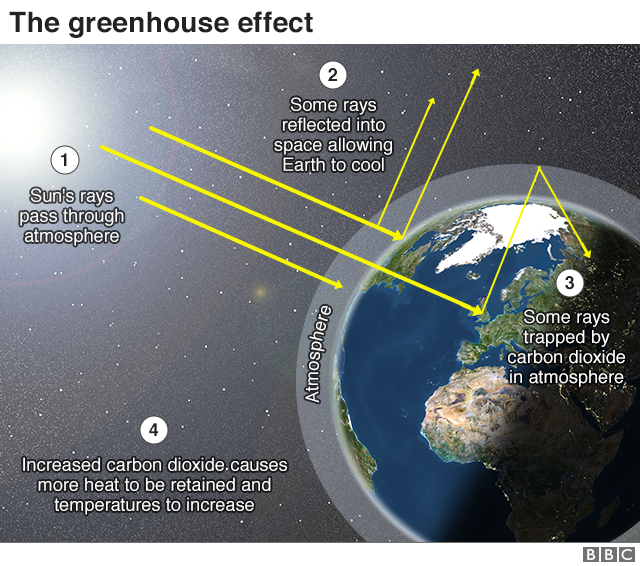
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsIn bright sunshine, the air inside a greenhouse becomes warm The greenhouse glass lets in the sun's light energy and some of its heat energy This heat builds up inside the greenhouse You just showed a small greenhouse effect What could happen if this greenhouse effect changed the Earth's climate? Some climate change skeptics dispute the socalled 'greenhouse effect', which keeps the surface temperature of the Earth approximately 33 degrees C warmer than it would be if there were no greenhouse gases in the atmosphere In other words, without the greenhouse effect, the Earth would be largely uninhabitable




Im Doing Environmental Science Questions But Im Not Chegg Com



Esa Greenhouse Effects Also On Other Planets
The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxidesDescribes how greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor, trap heat in the atmosphere, and that levels of these gases are increasing due to human activities Concept Map Discover related concepts in Math and Science CK12 Content Community ContentGreenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube
The term "greenhouse effect" is mentioned a lot when we talk about climate change But what exactly does it mean?How the greenhouse effect works Electromagnetic radiation at most wavelengths passes through the Earth's atmosphere The Earth absorbs most ofThe greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life



What Is Ocean Warming And Why Does It Matter Let S Talk Science




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
The average Earth temperature required for energy balance with the sun would be a frigid –18 °C (0 °F), if there were no atmospheric greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect has kept the Earth's average temperature a good deal higher for billions of years, making it Earth itself is similar to a greenhouse, which traps heat from the sun Because of this we experience the warm temperatures that we have on our planet Do some research to find out more about how The greenhouse effect occurs because the sun bombards Earth with enormous amounts of radiation that strike Earth's atmosphere in the form of visible light, plus ultraviolet (UV), infrared (IR) and




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach



Climate Change The Science Niwa
warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back to the surface byThe uncertainty lies in the magnitude of the responseIt is well established that the global mean surface temperature of the Earth has increased over the past century by about 06 KThis phenomenon, called the greenhouse effect, is naturally occurring and keeps the Earth's surface warm It is vital to our survival on Earth Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth's average surface temperature would be about 60° Fahrenheit colder, and our current way of life would be impossible




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




File Earth S Greenhouse Effect Us Epa 12 Png Wikimedia Commons
In short it is the natural process that warms the Earth's surface The process is called the greenhouse effect because the exchange of incoming and outgoing radiation that warms the planet works in a similar way to a greenhouse The greenhouse effect happens when these gases gather in the Earth's atmosphere According to scientists, without the greenhouse effect, the average temperature of the Earth would drop from 57 degrees Fahrenheit (14 degrees Celsius) to as low as negative 04 degrees F (minus 18 degrees C) Do We Blame the Industrial Revolution?Earth's natural greenhouse effect Earth's temperature begins with the Sun Roughly 30 percent of incoming sunlight is reflected back into space by bright surfaces like clouds and ice Of the remaining 70 percent, most is absorbed by the land and ocean, and the rest is absorbed by the atmosphere The absorbed solar energy heats our planet




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Earth S Outgoing Longwave Radiation Linear Due To H2o Greenhouse Effect Pnas
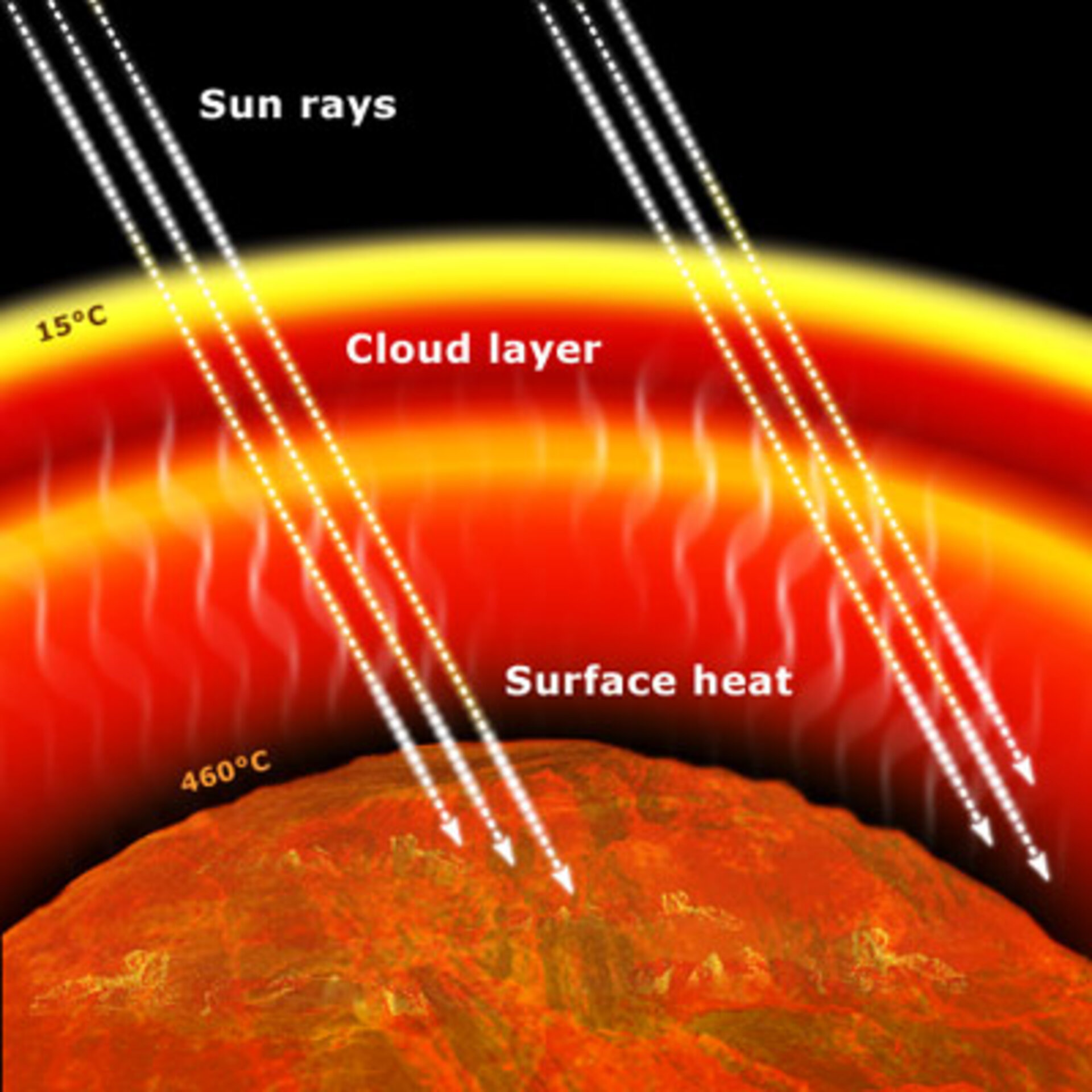
Sometime in the last few billion years, disaster struck one of Earth's nearest neighbours Planetary geologists think there is good evidence that Venus was the victim of a runaway greenhouseOn this page The natural greenhouse effect;If you made our Gummy Greenhouse Gas models, you may wonder why the molecules you made with gumdrops are called greenhouse gases Here is why If the atmosphere contains too much of these gases, the whole Earth becomes a hotter and hotter greenhouse




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Space
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-474143192-5b7df4fdc9e77c0050c92479.jpg)



Greenhouse Gas Effects On The Economy
Greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and reradiated by greenhouse gases The greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when gases in Earth's atmosphere trap the Sun's heat This process makes Earth much warmer than it would be without an atmosphere The greenhouse effect is one of the things that makes Earth a The impacts of global warming are already harming people around the world Now climate scientists have concluded that we must limit global warming to 15 degrees Celsius by 40 if we are to avoid



Http Www Campbellcountyschools Org Userfiles 1591 Greenhouse effect global warming lab Pdf
/https://public-media.si-cdn.com/filer/d2/95/d295d306-6ebf-4bfe-9471-70c73bb0d5ac/f11jcm_1.jpg)



This Suffrage Supporting Scientist Defined The Greenhouse Effect But Didn T Get The Credit Because Sexism Science Smithsonian Magazine
The natural greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect is a warming of the earth's surface and lower atmosphere caused by substances such as carbon dioxide and water vapour which let the sun's energy through to the ground but impede the passage of energy from the earthWhat exactly is the greenhouse effect?Radiation can be described as a flow of elementary particles, photons, each of which has a certain energy, proportional to the frequency of the radiation (see The thermal radiation of the black body)In the atmosphere, when a photon meets a molecule, it can capture its energy, but only under certain conditionsThe enhanced greenhouse effect refers to human activities that are adding to the warming of the atmosphere due to the greenhouse effect —the presence of gases that increases the atmosphere's retention of the heat energy of the sun




Greenhouse Effect Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia



1




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Greenhouse Effect Bioninja



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
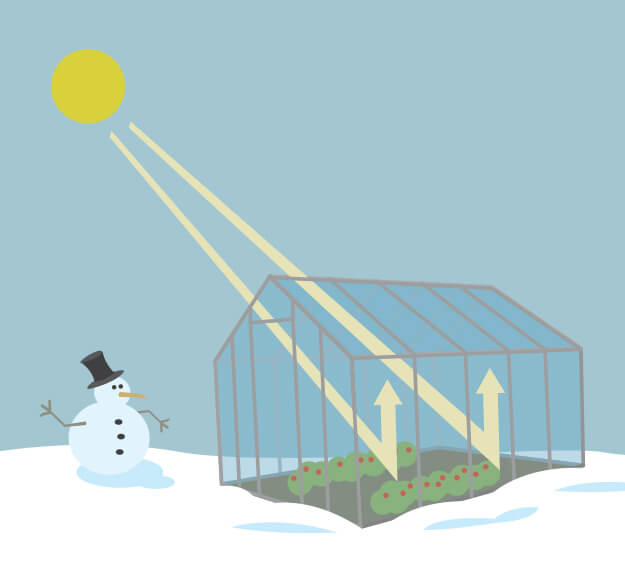




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Effect Aumsum Kids Science Education Children Youtube



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



3




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society




Climate Change Science And Impacts Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency



What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect
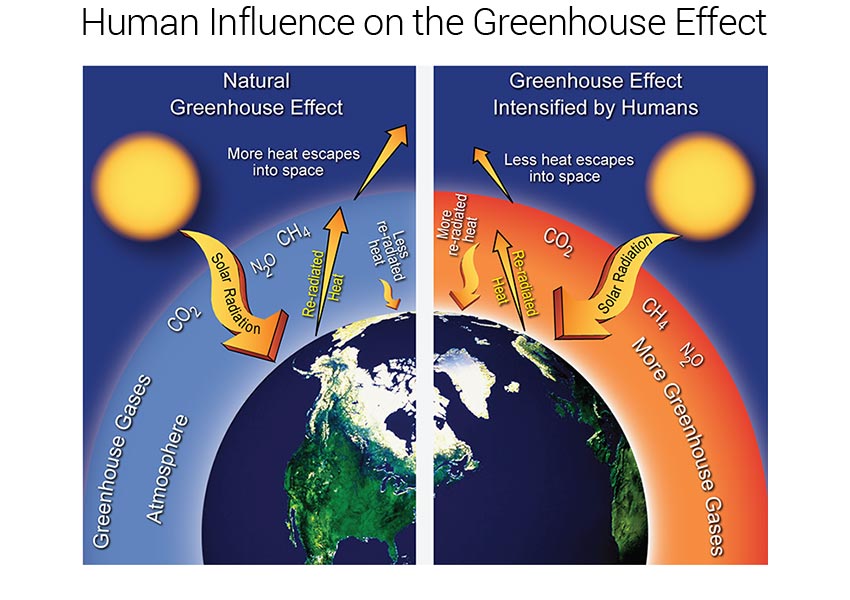



Climate Science Supplement National Climate Assessment




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia



1




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Greenhouse Effect Meaning Consequences And Impact Teachoo




Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate



Environment For Kids Global Warming




Pdf Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases And Their Impact On Global Warming



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




The Greenhouse Effect And Our Planet National Geographic Society




What Is Global Warming Live Science




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Scientists The Co2 Greenhouse Effect Was Cancelled Out By Clouds During 1992 14




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




Greenhouse Gas Ghg Meaning And Several Examples




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Lesson For Kids Study Com




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Curious




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects




Global Warming For Kids A Simple Explanation Of Climate Change



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
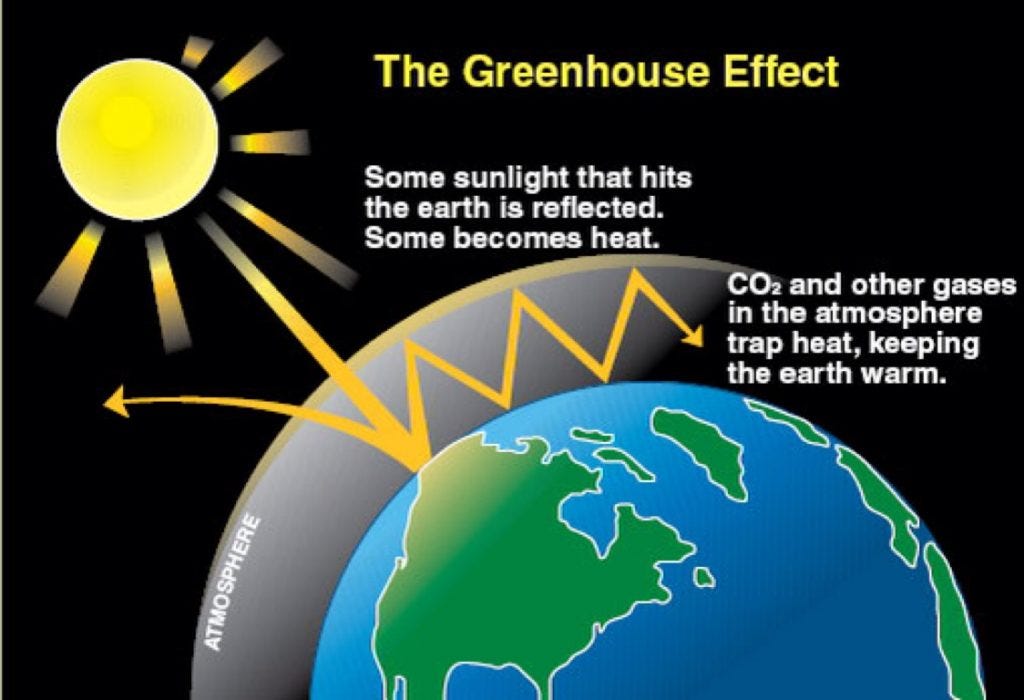



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium




Global Warming Definition And Meaning Market Business News




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
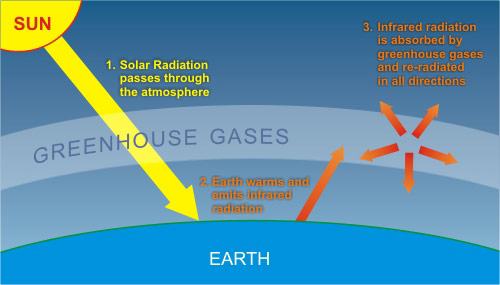



How Do We Know More Co2 Is Causing Warming



Greenhouse Effect Zoom Astronomy



Sources Sinks And Feedbacks National Geographic Society



The Greenhouse Effect
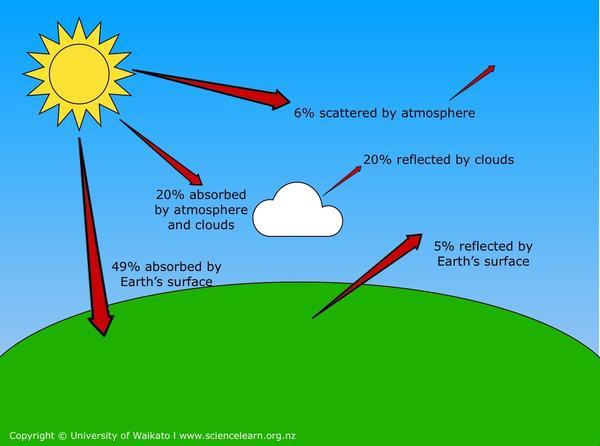



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub
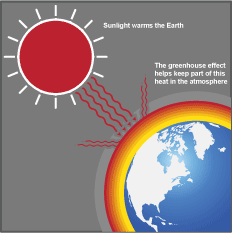



What Is The Greenhouse Effect What S Your Impact




What Is An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Universe Today




Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




Greenhouse Effect Teaching Box Ucar Center For Science Education




Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gases In Hindi How Green House Effect Works Youtube
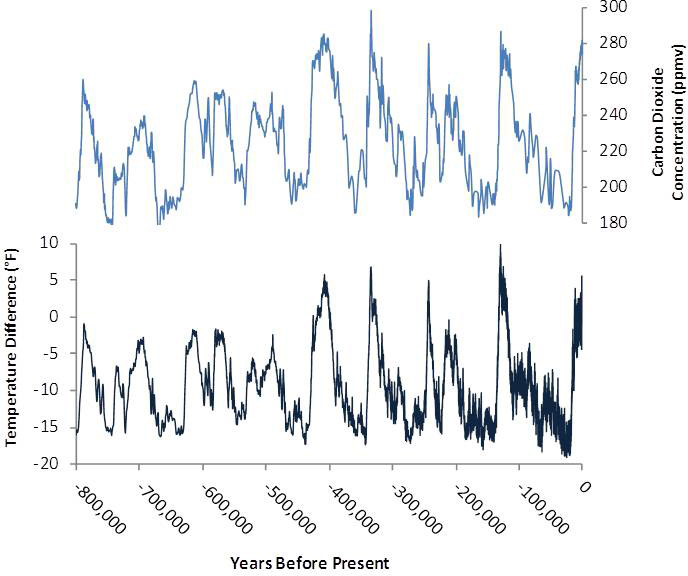



Causes Of Climate Change Climate Change Science Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Nasa S Climate Kids What Is The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Earth Science Homeschool Current Events For Kids




Greenhouse Effect Definition Easy To Understand



Methane Emissions In The Oil And Gas Industry American Geosciences Institute




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
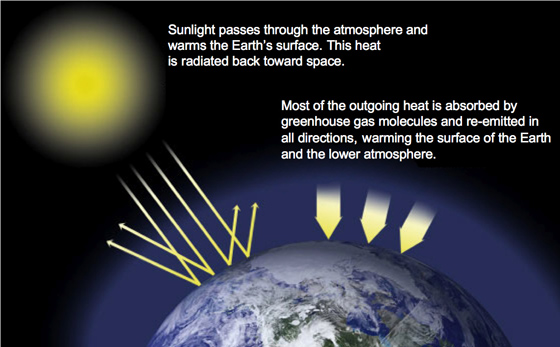



Climate Literacy Quiz




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Curious




Greenhouse Effect What Is It Definition And Role In Global Warming




The Greenhouse Effect Ucar Center For Science Education




Causes Of The Greenhouse Effect Conserve Energy Future




Weatherquestions Com What Is The Greenhouse Effect What Are Greenhouse Gases
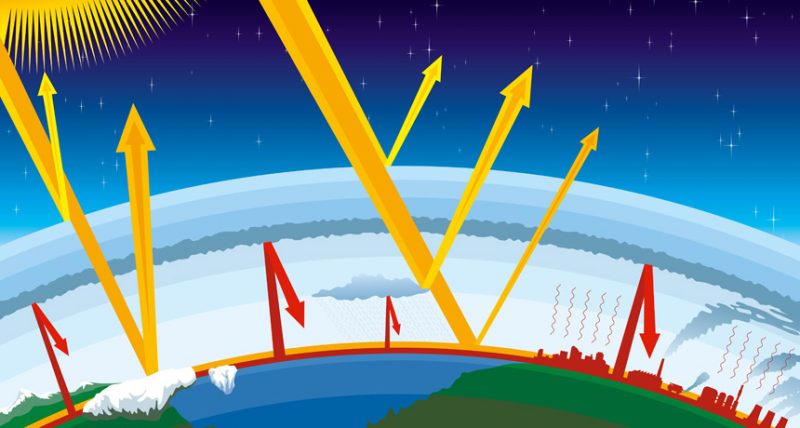




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Impermeable Earth Science Greenhouse Effect Warm Front
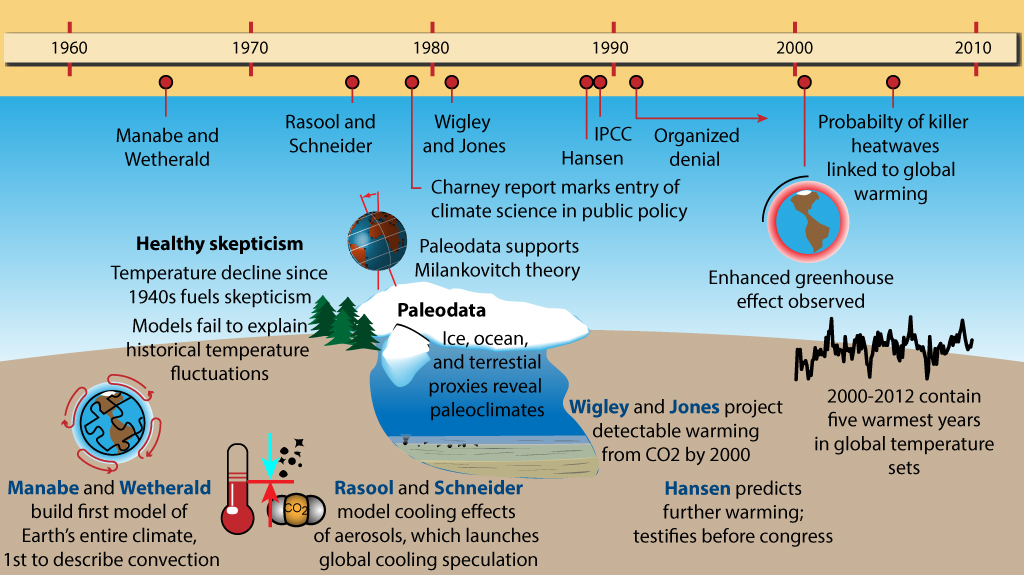



The History Of Climate Science



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿